Monitoring of reciprocating compressors
September 15, 2024
5 min of reading time
Preditec/IRM offers you the right technology for the protection, supervision and [...]

Preditec/IRM offers you the right technology for the protection, monitoring and diagnostics of your reciprocating compressors.
Reciprocating compressors are very critical machines in certain production processes. Therefore, the predictive strategy in their maintenance is essential to avoid:
- Unforeseen breakdowns that stop the production process.
- Catastrophic breakdowns that destroy the compressor.
- Decrease in performance.
Reciprocating machines are difficult to diagnose by vibration analysis. The FFT analysis technique that has been so successful in rotating machinery does not provide useful information for the diagnosis of the reciprocating machine. But there are other techniques also based on vibration measurement and analysis that have proven to be effective, such as waveform analysis. Vibration is usually measured on these machines as a global monitoring parameter as well as a diagnostic tool. The following diagram shows the main parameters for basic monitoring of reciprocating compressors:
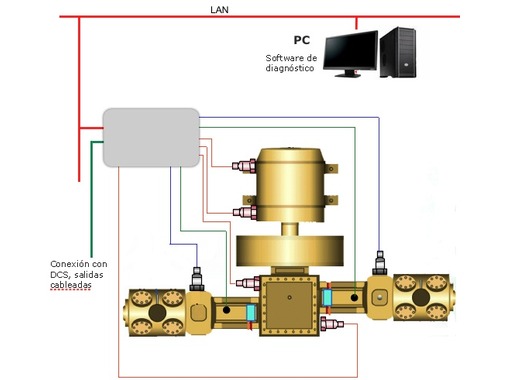
Vibration transmitters
By its very principle of operation, the reciprocating machine causes strong vibrations as it alternately displaces significant mass. Reciprocating compressor designs attempt to compensate for these forces to minimize vibration, but when a mismatch occurs, this vibration rises in amplitude. To detect these changes in vibration, they are mounted on the bedplate. vibration transmitters. These transmitters send to the distributed control system (DCS) the global value of the vibration in mm/s rms at various points of the compressor. This parameter will alert to structural problems or large misalignments that cause the compressor to vibrate above normal. The vibration velocity is very sensitive to changes in system stiffness or changes in exciting forces.
The vibration transmitters are placed on the compressor bed in a horizontal direction aligned with the direction of piston travel.
Impact transmitters
Backlash problems are best located by analyzing the measured acceleration waveform. This analysis can be performed manually, but if you want to automate it in a simple way you can use a impact transmitterspecially designed for this task. The impact transmitters measure high-frequency vibration (acceleration) and have an impact counter. Their integrated electronics transform the measured vibration wave into a scalar value indicating the number of times a set limit level has been exceeded in a certain configured time space. For each compressor, a vibration level and a usual number of times for the vibration wave to exceed the preset limit must be defined. This value is transmitted to the DCS for monitoring.
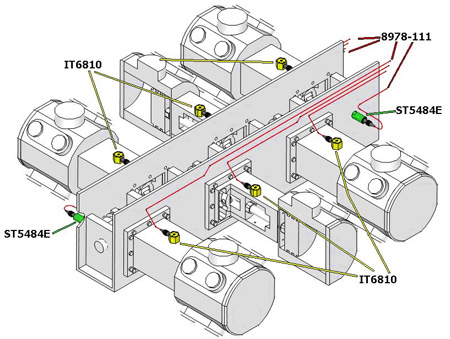
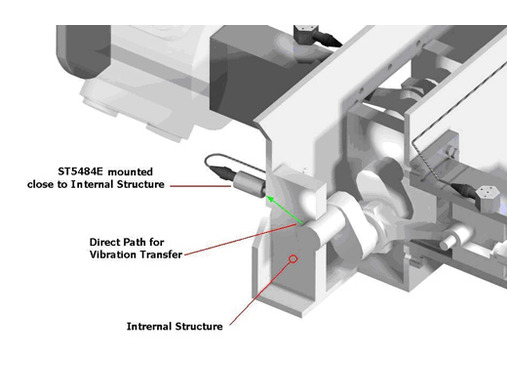
The impact transmitter is positioned near the crosshead and warns of mechanical problems such as looseness, rubbing or poor lubrication.
Although this is a recent technique, the installation of these impact transmitters has become widespread.
Stem drop
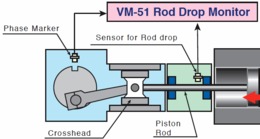 For rod drop monitoring, a proximity probe is placed to continuously measure the distance from a fixed point to the compressor rod. In this way a waveform is taken of the forward and return cycle of the connecting rod. Comparison over time of the recorded waveforms will alert to piston ring wear and other potential mechanical problems. Some rod drop monitoring systems are simplified by converting the proximity probe measurement to a scalar value. Depending on how this conversion is performed, the monitoring value is more or less reliable.
For rod drop monitoring, a proximity probe is placed to continuously measure the distance from a fixed point to the compressor rod. In this way a waveform is taken of the forward and return cycle of the connecting rod. Comparison over time of the recorded waveforms will alert to piston ring wear and other potential mechanical problems. Some rod drop monitoring systems are simplified by converting the proximity probe measurement to a scalar value. Depending on how this conversion is performed, the monitoring value is more or less reliable.
For the monitored parameter to be reliable, a point value must be taken every cycle outside the force reversal zones on the piston, therefore it is recommended that the measurement be synchronized with a tachometer.
Dynamic pressure analysis
But perhaps the technique that provides more information for the diagnosis of reciprocating compressors is the analysis of the dynamic pressure of each cylinder. The representation of the pressure over time of each cycle or the actual P-V diagram provides valuable information for the analysis of the compressor, both from point measurements made with portable equipment and for continuous monitoring.
Ultrasound analysis
Monitoring the condition of reciprocating compressor valves is critical due to the rate of compressor failures caused by valve problems. The technique that best indicates valve problems is the ultrasonic measurement at the cylinder head. The representation of the ultrasound wave along each cycle (360º of crankshaft) gives the necessary information for the localization of failures mainly in valves, but also the study of ultrasounds alerts us of other failures of mechanical origin, such as clearances in the crosshead, wear of segments, failures in the lubrication, etc.






