La estrategia predictiva en el mantenimiento industrial
1 septiembre 2024
2 min de lectura
En este artículo se analizan las distintas estrategias de mantenimiento [...]

En este artículo se analizan las distintas estrategias de mantenimiento aplicables a los activos industriales.
Descarga de Documentos
El interés principal de estas notas es servir a los responsables y coordinadores de mantenimiento industrial para acertar en la implantación de la estrategia correcta para cada activo y así conseguir un diseño óptimo de su plan de mantenimiento.
La aplicación de la estrategia predictiva en el mantenimiento industrial ha reportado enormes ahorros a aquellas compañías que han sabido aplicar las estrategias más adecuadas para cada activo. Pero la mayoría de instalaciones industriales programan las intervenciones de mantenimiento solamente tras un número de horas de funcionamiento o al aparecer una avería inesperada.
Las estrategias de gestión del mantenimiento que vamos a analizar son:
- Mantenimiento Regresivo
- Mantenimiento Reactivo
- Mantenimiento Preventivo
- Mantenimiento Predictivo
- Mantenimiento Proactivo
¿Mantenimiento predictivo o preventivo?
Mantenimiento programado según calendario o mantenimiento preventivo (PM)
El mantenimiento preventivo es aquel que programa la sustitución de los elementos de las máquinas de manera periódica antes de llegar al fin de su vida útil. La periodicidad de las intervenciones de mantenimiento se basa en cálculos teóricos o estimaciones de la duración de los componentes que fallan según patrones basados en el tiempo de funcionamiento.
Mantenimiento predictivo (PdM) o mantenimiento basado en la condición (CBM)
El mantenimiento predictivo o basado en la condición evalúa el estado de la maquinaria y recomienda intervenir o no, lo cual produce grandes ahorros en mantenimiento.
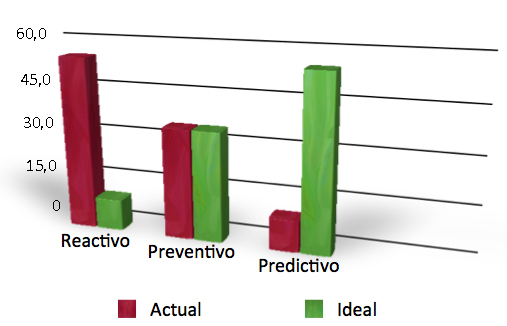
[…] El jefe de mantenimiento es quien ha de realizar los cambios necesarios para conseguir un equilibrio entre intervenciones de mantenimiento reactivas, preventivas y predictivas. Aunque los porcentajes entre ellos difieren de unos tipos de plantas industriales a otras, un objetivo general sería no tener en maquinaria crítica más de un 10% de intervenciones por reactivo, aproximadamente un 35% por preventivo y el resto (55%) por predictivo. La realidad de muchas plantas industriales es bastante diferente, lo cual influye negativamente en la rentabilidad global de la planta. […]